by Analog Devices, Inc.
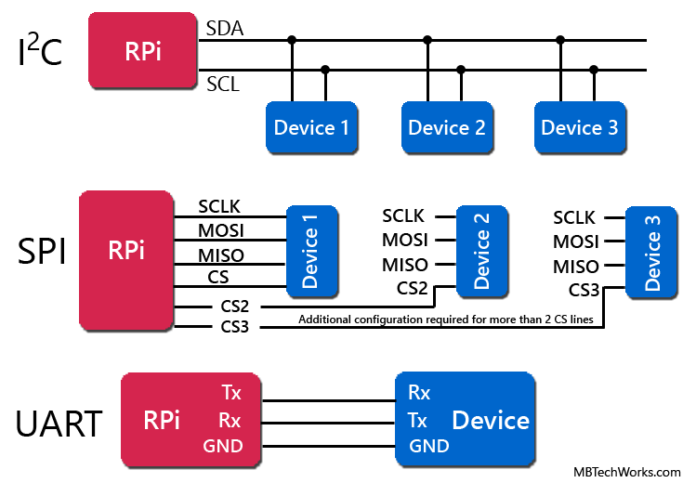
The serial peripheral interface (SPI) is one of the most widely used interfaces between microcontroller and peripheral ICs such as sensors, ADCs, DACs, shift registers, SRAM, and others. SPI is a synchronous, full duplex master-slave-based interface. The data from the master or the slave is synchronized on the rising or falling clock edge. Both master and slave can transmit data at the same time. The SPI interface can be either 3-wire or 4-wire.
This article provides a brief description of the 4-wire SPI interface followed by an introduction to SPI enabled switches and muxes that help reduce the number of digital GPIOs in system board design.
References:
- ADuCM3029 data sheet. Analog Devices, Inc., March 2017.
- Nugent, Stephen. “Precision SPI Switch Configuration Increases Channel Density.” Analog Dialogue, May 2017.
- Usach, Miguel. AN-1248 Application Note: SPI Interface. Analog Devices, Inc., September 2015.
End Of Post