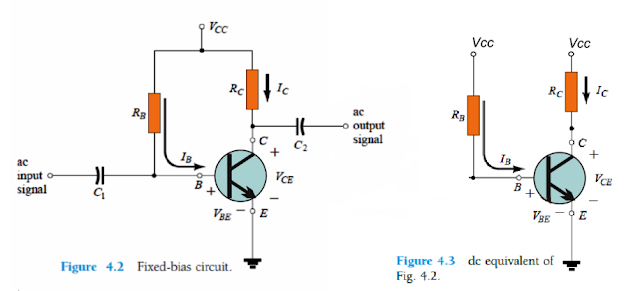
In simple terms, biasing in BJTs may be defined as a process in which a BJT is activated or switched ON by applying a smaller magnitude of DC is across its base/emitter terminals so that its is able to conduct a relatively larger magnitude of DC across its collector emitter terminals.
The working of a Bipolar transistor or BJTs at DC levels is governed by several factors, that includes a range of operating points over the characteristics of the devices.
Under the section 4.2 explained in this article we will check the details regarding this range of operating points for BJT amplifiers. Once the specified DC supplies are calculated, a circuit design may be created for determining the required operating point.
A variety of such configurations are examined within this article. Every single model discussed will in addition identify the stability of the approach, meaning, exactly how sensitive the system could be to a given parameter.
Although numerous networks are examined within this section, they have one fundamental similarity between the assessments of each configuration, because of the following repeated use of the crucial fundamental relationship:
Ed Of Post